
Your doctor might ask for all of these tests, or for just 1 or 2 of them.

Having too much iron in your body can cause damage to your: heart, liver, pancreas and joints.
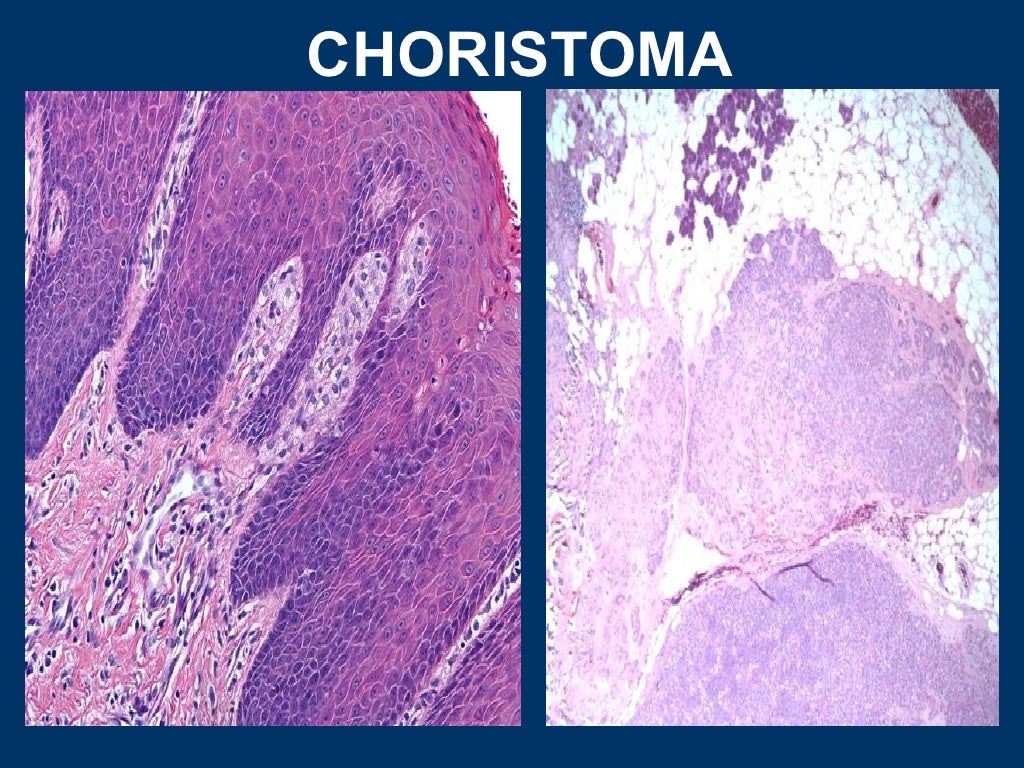
#Pathology definition full
Anaemia can be detected by a full blood count. This can lead to a condition called anaemia. New blood cells are needed to replace blood that you lose from: When you don't have enough iron in your body, you may have difficulty making new blood cells. In particular, iron is a vital part of haemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells that helps carry oxygen around your body. Iron is an essential part of many cells in your body, including your blood and muscle cells. Related information on Australian websites.Your doctor will explain your test results.
Having either too little or too much iron can cause serious health problems.Iron studies are blood tests that look at how much iron is in your body.A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z A Abscess Acanthosis Acute inflammation Addendum Adenoma Adenocarcinoma Adenomyosis Adenosquamous carcinoma Adipose tissue Adrenal gland AE1/AE3 Amendment Anaplastic Anemia Angioinvasion Antral type mucosa Antibody Apocrine Apoptosis Arteriovenous malformation (AVM) Atrophic Atrophy Atypia Atypical Atypical mitotic figure Atypical mitosis B B cells Ballooning hepatocyte Basal lymphoplasmacytosis Basaloid neoplasm Basophils Benign Benign neoplasm Biopsy Body type mucosa BRAF Breast cancer Breslow thickness C Calcification Carcinoma Carcinoma in situ Carcinoid Cautery artifact CD19 CD20 CD3 CD30 CD34 CD45 CD5 CD68 CDX-2 Cholesterol cleft Chronic inflammation Chromatin Chromogranin Colon Colon cancer Colonic mucosa Columnar mucosa Cribriform Crohn’s disease Crypt abscess Crypt distortion Cryptitis Cytokeratin Cytokeratin 5 (CK5) Cytokeratin 7 (CK7) Cytokeratin 20 (CK20) Cytologic atypia Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Cyst Cytoplasm D Degenerative changes Desmin Desmoplasia DIF Differentiated Diffuse Direct immunofluorescence Distal Duct Dysplasia E E-cadherin Edema Endophytic Eosinophil Epithelial cell Epithelium Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNAs (EBER) Estrogen receptor (ER) Erosion Excision Exophytic Extranodal extension (ENE) Extraparenchymal extension F Fat necrosis Fibrosis Fibrinoid necrosis Fibrinopurulent exudate Fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) FISH Flow Fluorescence in situ hybridization Foamy histiocyte Focal Foveolar metaplasia Frozen section Fuhrman grade G GATA-3 Gallbladder Gastric heterotopia Gland Grade Granulation tissue Granuloma Grocott (GMS) Gross Gross description H Hamartoma HBME-1 Helicobacter pylori H. Visit our Diagnosis Library to learn more about your diagnosis.

These definitions describe general concepts. The pathology dictionary is a collection of patient-friendly definitions for the most common terms and phrases used by pathologists in pathology reports.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
